Solid Spectroscopy Hosting Architecture of Databases and Expertise
Solid Spectroscopy Hosting Architecture of Databases and Expertise
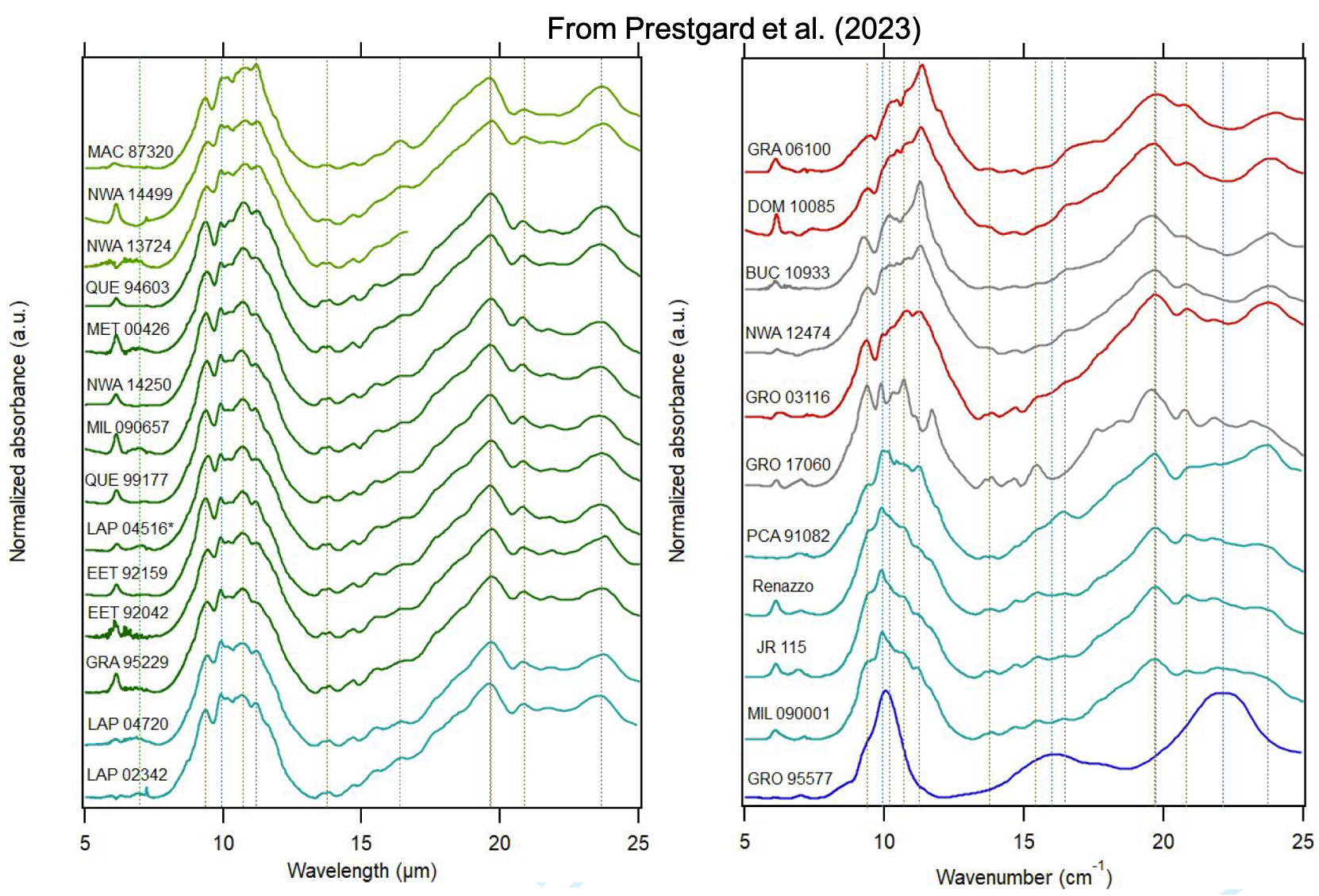
SSHADE is an interoperable Solid Spectroscopy database infrastructure (www.sshade.eu) providing spectral and photometric data obtained by various spectroscopic techniques over the whole electromagnetic spectrum from gamma to radio wavelengths, through X, UV, Vis, IR, and mm ranges. The measured samples include ices, minerals, rocks, organic and carbonaceous materials... and also liquids. They are either synthesized in the laboratory, natural terrestrial analogs collected or measured in the field, or extraterrestrial samples collected on Earth or on planetary bodies: (micro-)meteorites, IDPs, lunar soils...
SSHADE contains a set of specialized databases from various research groups, mostly from Europe. It is developed under the H2020 European programs* "Europlanet 2020 RI" and now "Europlanet 2024 RI" with the help of OSUG, CNRS/INSU, IPAG, and CNES. It is hosted by the OSUG data center / Université Grenoble Alpes, France. It can also be searched through the Virtual European Solar and Planetary Access (VESPA) virtual observatory.
(*) Europlanet 2020 RI and Europlanet 2024 RI have received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreements N°654208 and N°871149